The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says heart disease is the main cause of death in the United States. As February is American Heart Month, now is a great time to learn more about cardiovascular (heart) disease and how you can protect yourself against it.
Types of Cardiovascular Disease
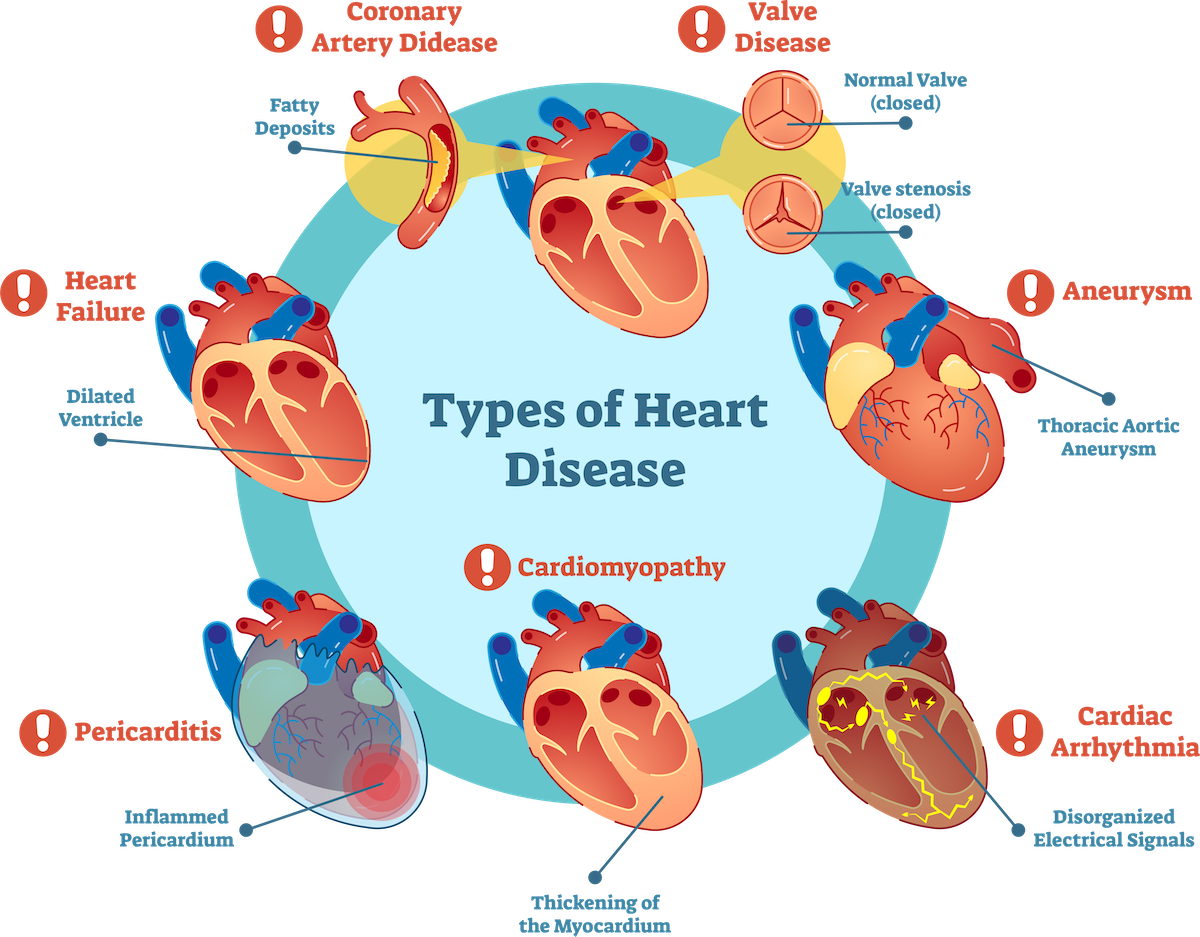
There are a number of types of heart disease with multiple causes. Many times, a process called atherosclerosis is part of the problem. Atherosclerosis happens when a fatty material called plaque builds up on the inside walls of the arteries making it hard for blood to move through them. The arteries are tubes that carry blood from the heart to other parts of the body. Atherosclerosis can cause symptoms of heart disease like heart attacks and angina (chest pain).
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary Artery Disease, or CAD, is caused by atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries carry blood to the heart. When plaque in the arteries makes it hard for blood to move through them, a heart attack can happen. CAD is the most common cause of heart attacks. It can also lead to heart failure. According to the CDC, around 18.2 million adults age 20 and over have CAD.
Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure is a serious and long-term condition that gets worse over time. Heart failure does not mean that the heart stops working completely. It means that the heart no longer works as well as it should.
To make up for this, the heart may start pumping faster and get bigger. It becomes larger by stretching out to pump the blood harder and develops more muscle to help it beat. Eventually, the heart can’t keep up, and the person may feel really tired or have a lot of trouble breathing.
Heart Valve Disease
The heart has four valves that keep blood moving in the right direction. As the heart muscle beats, the valves open and close. Heart valve disease happens when one or more of the valves in a person’s heart do not work how they should. Some of the things that can cause heart valve disease are:
- Stenosis: The flaps of the heart valves become too thick or stiff and do not open right which makes it hard for blood to flow through
- Regurgitation: The flaps of the valve do not close right. This causes blood to leak backward into the heart
- Atresia: Instead of the opening and closing of the valves, a solid piece of tissue blocks blood flow
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a type of heart disease that can cause the muscle tissue to become weak, making it harder for the heart to pump blood in the right way. Cardiomyopathy may cause you to have heart valve problems and/or heart failure.
Heart Arrhythmia
Heart arrhythmia is when the heart doesn’t beat as it should – either by beating too fast or too slow. It is normal for your heart to slow down during rest and speed up during stress. However, there are other cases where an unusual heartbeat may be a more serious problem. Some people are born with this condition while others can develop it over time. Untreated arrhythmia can result in cardiac arrest and/or stroke.
Pericarditis
A thin layer of tissue called the pericardium surrounds your heart. Its job is to hold your heart in place and help it work properly. Pericarditis happens when the pericardium becomes inflamed or swollen. This condition can be acute (happens suddenly and goes away quickly) or chronic (happens slowly and takes longer to fix). Untreated pericarditis can lead to heart failure.
Signs & Symptoms
Some people with heart disease feel symptoms and others do not until they have a heart attack. It is important to know that even if you feel fine, you could have problems with your heart that you do not know about.
If you do have symptoms, you may feel things like:
- Tiredness
- Chest pain
- Pain in the back or left arm
- Trouble breathing
- A fast heartbeat
- Having to throw up
Women often have different symptoms than men like:
- Trouble sleeping
- Stomach ache after eating
- Sweating
- Feeling weak
- Feeling dizzy
- Tiredness
- Chest pain
Risk Factors
There are certain things that can increase your chances of getting heart disease. Some of these things you can control, and others you cannot –
- High blood pressure
- Unhealthy blood cholesterol levels
- Family history of heart problems
- Diabetes
- Being overweight
- Smoking
- Age
- Not exercising enough
Diagnosing Cardiovascular Disease
One of the best ways to protect yourself from heart disease is to get screened. There are different tests available that can find problems with your heart early. When problems with your heart are found early, they are usually easier to treat. At UDMI, we do the following screening tests for heart disease:
- Coronary CT Angiography (CCTA): A CT scan used to view the arteries that carry blood to the heart. If there is plaque, this exam will show the radiologist where it is
- CT Calcium Scoring: A CT scan used to measure how much plaque there is in the arteries
- Abdominal Aorta Ultrasound: An ultrasound exam used to look at the aorta. The aorta is the biggest artery in the body and it carries blood from the heart to other parts of your body
- Echocardiography: An ultrasound exam used to look at the heart muscle and valves to see how well blood is moving through your heart
- Carotid Ultrasound: An ultrasound used to look at the carotid arteries. The carotid arteries are in your neck and they carry blood from the heart to your brain
Your health insurance may pay for you to get heart disease screening. Call them to ask. If they tell you they will not pay for it, it may be smart for you to get it anyway.
If the screening test(s) show that you may have a problem with your heart, your doctor may refer you for more tests at UDMI like:
- Nuclear stress test: An imaging exam that uses a special camera to look at blood supply to the heart when it is at rest and when it is most active (or under “stress). To create this “stress”, you will be asked to run on the treadmill for a short period of time. If you can’t run on the treadmill, you will be given a shot with medicine that will make your heart beat fast
- Chest XRAY: An X-RAY exam used to look at the heart, lungs, and blood vessels
- MUGA Scan: An imaging exam that uses a special camera to take pictures of the heart as it pumps blood
Knowing your risks and being tested for heart disease can save your life. For more information on screenings for cardiovascular disease or to schedule an appointment, call 718-931-5620 or submit a request on our website. Note: A written referral from your doctor is required.










